Using Spreadsheet JSF Component
Available in ZK Spreadsheet EE only
Overview
In this section, we will demonstrate how to make other JSF components interact with Spreadsheet in a JSF page using the AJAX tag. We assume that you know some basics about JSF including life cycle, tag usage, event handling, AJAX tag, and managed bean.
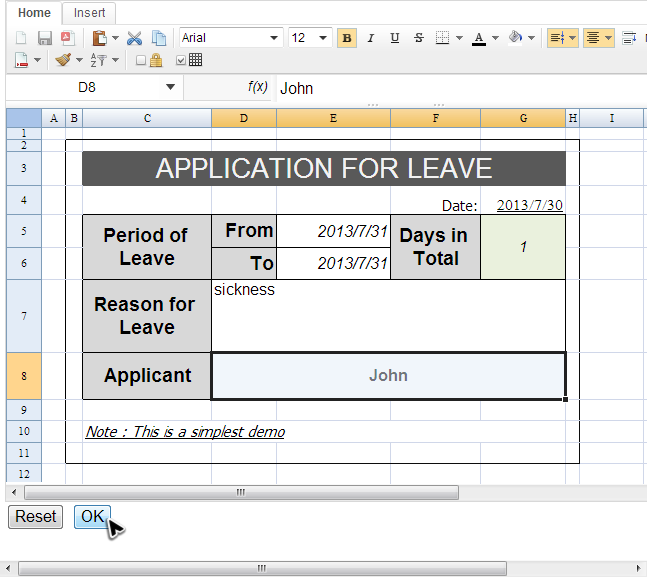
The example application is a simple page to request for leave. A user fills the required field in cells and click "OK" button to submit his request for leave. Or he can clicks "Reset" button to reset what he inputs to default value. The screenshot below shows a request of a user "John":
Create a JSF Page
Spreadsheet can be embedded in a JSF page in the same way as JSF standard components. First specify ZK Spreadsheet component namespace URI http://www.zkoss.org/jsf/zss declaration along with other JSF namespace declarations and you can use the tag like <zssjsf:spreadsheet/>. If we want to interact with Spreadsheet in JSF AJAX tag, we should also put a <zssjsf:update/> component which is invisible in the browser in on the same page to process ZK AU response.
Let's see the JSF page of our example application.
app4l.xhtml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:zssjsf="http://www.zkoss.org/jsf/zss"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html">
<h:head>
<title>Application for Leave</title>
<zssjsf:head/>
</h:head>
<h:body>
<h:form id="form">
<div>
<zssjsf:spreadsheet id="myzss"
book="#{applicationForLeave.book}"
actionBridge="#{applicationForLeave.actionBridge}"
width="800px" height="500px"
maxVisibleRows="50" maxVisibleColumns="20"
showToolbar="true" showFormulabar="true"
showContextMenu="true" showSheetbar="true"/>
<h:panelGrid columns="3">
<h:commandButton value="Reset"
action="#{applicationForLeave.doReset}" >
<f:ajax execute="@all" render="msg zkupdate"/>
</h:commandButton>
<h:commandButton value="Ok"
action="#{applicationForLeave.doOk}">
<f:ajax execute="@all" render="msg zkupdate" />
</h:commandButton>
<h:messages id="msg"/>
</h:panelGrid>
</div>
<zssjsf:update id="zkupdate"/>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
- Line 16: ZK Spreadsheet JSF component tag supports all the properties that are supported by Spreadsheet ZUL component tag.
- Line 17: The
bookattribute is used to bind a Book to spreadsheet from a managed bean. - Line 18: The
actionBridgeattribute is only available on Spreadsheet JSF component which is used to set an ActionBridge to a managed bean. This object will be explained in next section. - Line 25, 29: We use JSF's AJAX tag to trigger event handler methods defined in our managed bean. The component ID in
executeattribute must includezssjsf:spreadsheetID, and here we use@alljust for convenience. Therenderattribute must includezssjsf:updateID. - Line 35: The
updateis another JSF component provided by ZK Spreadsheet which is responsible for processing ZK AU response.
Managed Bean
It's a standard practice to bind a JSF component with a managed bean which contains data model and business logic. Spreadsheet JSF component obtains Book object from attribute book and set ActionBridge to a managed bean's actionBridge
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class ApplicationForLeave {
// the book of spreadsheet
private Book book;
//the bridge to execute action in ZK context
private ActionBridge actionBridge;
private String dateFormat = "yyyy/MM/dd";
public Book getBook() {
if (book != null) {
return book;
}
try {
URL bookUrl = FacesContext.getCurrentInstance()
.getExternalContext()
.getResource("/WEB-INF/books/application_for_leave.xlsx");
book = Importers.getImporter().imports(bookUrl, "app4leave");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
Locales.setThreadLocal(Locale.getDefault());
Sheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
// reset sample data
// you can use a cell reference to get a range
Range from = Ranges.range(sheet, "E5");// Ranges.range(sheet,"From");
// or you can use a name to get a range (the named range has to be set in book);
Range to = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "To");
Range reason = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "Reason");
Range applicant = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "Applicant");
Range requestDate = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "RequestDate");
// use range api to set the cell data
from.setCellEditText(DateUtil.tomorrow(0, dateFormat));
to.setCellEditText(DateUtil.tomorrow(0, dateFormat));
reason.setCellEditText("");
applicant.setCellEditText("");
requestDate.setCellEditText(DateUtil.today(dateFormat));
return book;
}
public void setBook(Book book) {
this.book = book;
}
public ActionBridge getActionBridge() {
return actionBridge;
}
public void setActionBridge(ActionBridge actionBridge) {
this.actionBridge = actionBridge;
}
...
}
- Line 12,20: Import a file for a Spreadsheet.
- Line 56: The
actionBridgewill be set by Spreadsheet JSF component.
Implement Event Handler Method
In JSF, we can use the syntax below to invoke an event handler method, doReset(), of a managed bean ( applicationForLeave) in AJAX request.
<h:commandButton value="Reset" action="#{applicationForLeave.doReset}" >
<f:ajax execute="@all" render="msg zkupdate" />
</h:commandButton>
Because of accessing ZK components like Spreadsheet needs to be in a ZK execution, we can use ActionBridge to help us. One new ActionBridge object is provided by Spreadsheet JSF component for each request to a managed bean via setter. All we have to do is to specify in actionBridge attribute with a managed bean's property like:
<zssjsf:spreadsheet id="myzss"
actionBridge="#{applicationForLeave.actionBridge}" .../>
Then, we can use this ActionBridge to execute our business logic: reset and check cells.
Handling Spreadsheet Data Model
Inside ActionBridge.execute(), you can use those APIs we mentioned in Handling Data Model to implement your business logic. In our example, we use Range to set cell edit text and get value from cells.
doReset()
The usage of ActionBridge is to call its execute() with an Action object and we implement our business logic in Action's execute() method with those APIs mentioned in previous sections. In "reset cells" case, we use Range to clear cell text.
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class ApplicationForLeave {
...
public void doReset() {
//use actionBridge to execute the action inside zk context
//so the spreadsheet can get the update of book automatically
actionBridge.execute(new Action() {
public void execute() {
Sheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
// reset sample data
// you can use a cell reference to get a range
Range from = Ranges.range(sheet, "E5");// Ranges.range(sheet,"From");
// or you can use a name to get a range (the named range has to be
// set in book);
Range to = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "To");
Range reason = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "Reason");
Range applicant = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "Applicant");
Range requestDate = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet, "RequestDate");
// use range api to set the cell data
from.setCellEditText(DateUtil.tomorrow(0, dateFormat));
to.setCellEditText(DateUtil.tomorrow(0, dateFormat));
reason.setCellEditText("");
applicant.setCellEditText("");
requestDate.setCellEditText(DateUtil.today(dateFormat));
}
});
addMessage("Reset book");
}
private void addMessage(String message){
FacesContext.getCurrentInstance().addMessage(null, new FacesMessage(message));
}
}
- Line 10: Handling an events by passing an
Actionobject implemented with your business logic toActionBridge'sexecute(). - Line 11: Override
Action'sexecute()to implement clearing cell texts.
Then ActionBridge will response corresponding update script to update the Spreadsheet in app4l.xhtml.
doOK()
The same rule applies to "doOK()" method, and we just list codes of Action for your reference.
@ManagedBean
@RequestScoped
public class ApplicationForLeave {
...
public void doOk() {
//access cell data
actionBridge.execute(new Action() {
public void execute() {
Sheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
Date from = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"From").getCellData().getDateValue();
Date to = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"To").getCellData().getDateValue();
String reason = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"Reason").getCellData().getStringValue();
Double total = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"Total").getCellData().getDoubleValue();
String applicant = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"Applicant").getCellData().getStringValue();
Date requestDate = Ranges.rangeByName(sheet,"RequestDate").getCellData().getDateValue();
//validate input
if(from == null){
addMessage("FROM is empty");
}else if(to == null){
addMessage("TO is empty");
}else if(total==null || total.intValue()<0){
addMessage("TOTAL small than 1");
}else if(reason == null){
addMessage("REASON is empty");
}else if(applicant == null){
addMessage("APPLICANT is empty");
}else if(requestDate == null){
addMessage("REQUEST DATE is empty");
}else{
//Handle your business logic here
addMessage("Your request are sent, following is your data");
addMessage("From :" +from);
addMessage("To :" + to);
addMessage("Reason :"+ reason);
addMessage("Total :"+ total.intValue());//we only need int
addMessage("Applicant :"+ applicant);
addMessage("RequestDate :"+ requestDate.getTime());
//You can also store the book, and load it back later by exporting it to a file
Exporter exporter = Exporters.getExporter();
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
File temp = File.createTempFile("app4leave_", ".xlsx");
fos = new FileOutputStream(temp);
exporter.export(sheet.getBook(), fos);
System.out.println("file save at "+temp.getAbsolutePath());
addMessage("Archive "+ temp.getName());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if(fos!=null)
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
//handle the exception
}
}
}
}
});
}
}
Source Code of Example
Source code of above example application can be accessed in github.
All source code listed in this book is at Github.